Turinys
Medical treatments for tuberculosis
Diagnostinis
During the active phase of the disease, symptoms are usually present (fever, night sweats, persistent cough, etc.). The doctor relies on these symptoms, but also on the results of the following tests and examinations.
Odos testas. The skin test can detect the presence of Koch’s bacillus in the body. In a newly infected person, this test will be positive 4 to 10 weeks after infection. A tiny amount of tuberculin (a purified protein from Mycobacterium tuberculosis) is injected under the skin. If a skin reaction occurs at the injection site (redness or swelling) over the next 48 to 72 hours, this indicates infection. If the result is negative, the doctor may suggest a second test a few weeks later.
Medical treatments for tuberculosis: understand everything in 2 minutes
Pulmonary radiography. If the patient has symptoms of a persistent cough, for example, a chest x-ray will be ordered to assess the condition of the lungs. During the follow-up, the x-ray also makes it possible to check the progress of the disease.
Biological tests on pulmonary secretion samples. The secretions are first observed under a microscope to check whether the bacteria present in the secretions are part of the mycobacteria family (Koch’s bacillus is a mycobacterium). The result of this test is obtained the same day. We also proceed to the kultūra of secretions to identify bacteria and whether or not they are resistant to antibiotics. However, you have to wait 2 months to get the results.
If the microscopic test reveals the presence of mycobacteria and the medical evaluation suggests that it is tuberculosis, treatment with antibiotics is started without waiting for the result of the microbial culture test. Thus, the symptoms are relieved, the disease is controlled, and the person is less likely to transmit the infection to those around them. The treatment can then be corrected, if necessary.
Antibiotic treatments
Šios first-line antibiotics can beat tuberculosis in almost all cases. People with the condition are asked to stay at home or wear a mask in public until the doctor determines they are no longer contagious (usually after two or three weeks of treatment).
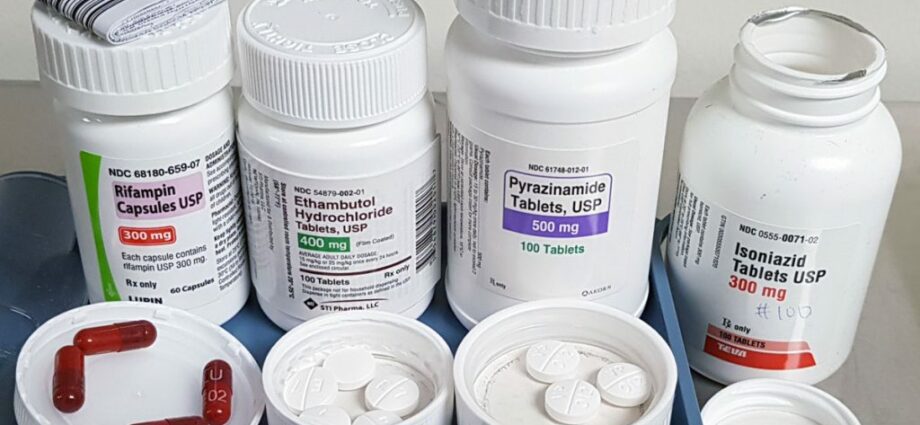
First line treatment. Usually prescribed four antibiotics the following are isoniazid, rifampin, ethambutol and pyrazinamide, which are taken by mouth. To be effective and to completely kill bacteria, medical treatment requires that the drugs be taken daily for a minimum period of time. 6 mėnesių, sometimes up to 12 months. All of these antibiotics can cause liver damage to varying degrees. Tell your doctor if any symptoms occur, such as nausea and vomiting, loss of appetite, jaundice (a yellowish complexion), dark urine, or fever for no apparent cause.
Second line treatments. If the bacteria are resistant to the two main antibiotics (isoniazid and rifampin), then it is called multidrug resistance (MDR-TB) and it is necessary to resort to drugs of 2e line. Sometimes 4 to 6 antibiotics are combined. They often need to be taken over a longer period, sometimes up to 2 years. They can also cause side effects, for example, numbness in the hands or feet, and liver toxicity. Some of them are administered intravenously.
Treatments for ultra-resistant bacteria. If the strain of infection is resistant to several treatments normally offered on the first or second line, a more severe and more toxic treatment, often administered intravenously, is used to fight against this so-called extensively resistant tuberculosis or XDR-TB.
Trūkumai-indikacijos. THE 'alkoholis iracetaminofenas (Tylenol®) are contraindicated throughout the treatment. These substances put more strain on the liver and can cause problems.
kitas
Tuo atveju'Maistas deficient, taking a multivitamin and mineral supplement may help prevent the infection from coming back4. The adoption of more balanced eating habits should be favored in order to accelerate recovery, when possible. For more details on the basics of healthy eating, see our Eat Better section.
Svarbi. Even if the disease is no longer contagious after 2 or 3 weeks of treatment, it should be continued for all the prescribed duration. Incomplete or inappropriate treatment is worse than no treatment. Indeed, treatment interrupted before term can lead to the spread of bacteria resistant to antibiotics. The disease is then much more difficult and time consuming to treat, and the treatments are more toxic to the body. In addition, it is a major cause of death, particularly among people infected with HIV. Finally, if the bacteria become resistant is transmitted to other people, the preventive treatment is then ineffective. |