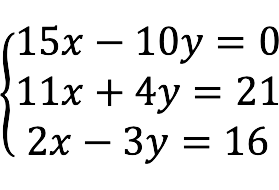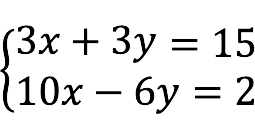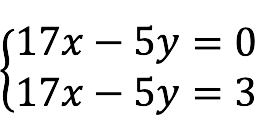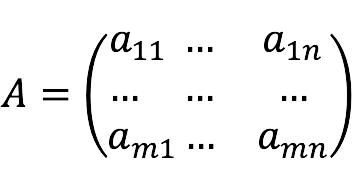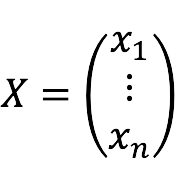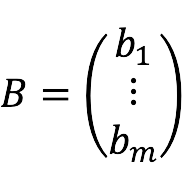Turinys
In this publication, we will consider the definition of a system of linear algebraic equations (SLAE), how it looks, what types there are, and also how to present it in a matrix form, including an extended one.
Definition of a system of linear equations
Tiesinių algebrinių lygčių sistema (or “SLAU” for short) is a system that generally looks like this:
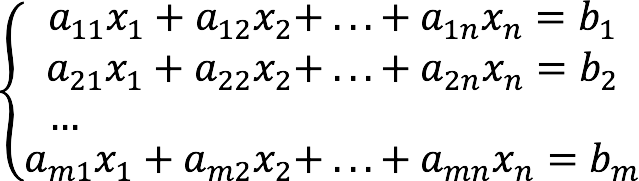
- m is the number of equations;
- n is the number of variables.
- x1, x2,…, xn – unknown;
- a11,12…, amn – coefficients for unknowns;
- b1, b2,…, bm – free members.
Coefficient indices (aij) are formed as follows:
- i is the number of the linear equation;
- j is the number of the variable to which the coefficient refers.
SLAU solution – such numbers c1C2,…, cn , in the setting of which instead of x1, x2,…, xn, all equations of the system will turn into identities.
Types of SLAU
- Vienalytis – all free members of the system are equal to zero (b1 =b2 = … = bm = 0).

- Nevienalytis – if the condition above is not met.
- aikštė – the number of equations is equal to the number of unknowns, i.e.
m = n .
- Underdetermined – the number of unknowns is greater than the number of equations.

- nepaisoma There are more equations than variables.

Depending on the number of solutions, SLAE can be:
- Bendras has at least one solution. Moreover, if it is unique, the system is called definite, if there are several solutions, it is called indefinite.

The SLAE above is joint, because there is at least one solution:
x = 2 , y = 3. - nesuderinamas The system has no solutions.

The right sides of the equations are the same, but the left ones are not. Thus, there are no solutions.
Matrix notation of the system
SLAE can be represented in matrix form:
AX = B
- A is the matrix formed by the coefficients of the unknowns:

- X – column of variables:

- B – column of free members:

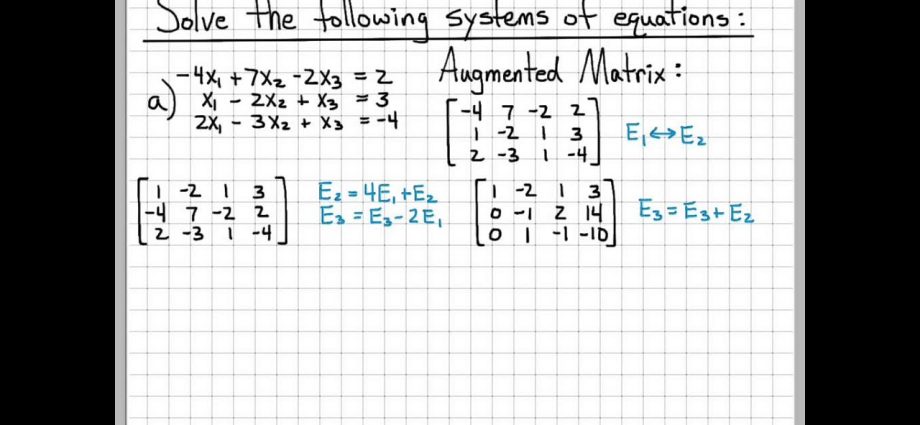
Pavyzdys
We represent the system of equations below in matrix form:
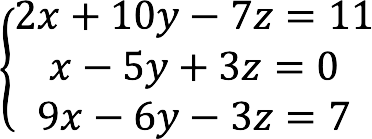
Using the forms above, we compose the main matrix with coefficients, columns with unknown and free members.
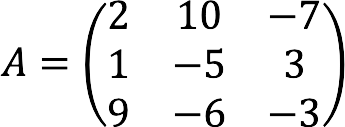
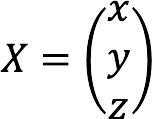
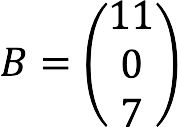
Complete record of the given system of equations in matrix form:
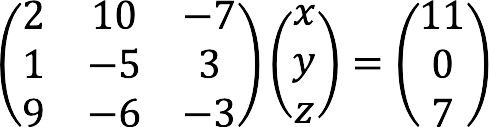
Extended SLAE Matrix
If to the matrix of the system A add free members column to the right B, separating the data with a vertical bar, you get an extended matrix of SLAE.
For the example above, it looks like this:
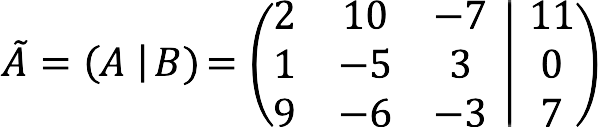
![]() – designation of the extended matrix.
– designation of the extended matrix.